Unpacking Africa’s Population Landscape: A Look at Density Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Unpacking Africa’s Population Landscape: A Look at Density Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking Africa’s Population Landscape: A Look at Density Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking Africa’s Population Landscape: A Look at Density Maps and Their Significance

Africa, the second-largest and second-most populous continent, presents a complex and dynamic demographic landscape. Understanding the distribution of its population is crucial for effective planning and resource allocation, particularly in the face of rapid urbanization and environmental challenges. Population density maps, visual representations of population distribution per unit area, provide valuable insights into this intricate picture.
Decoding the Map: Unveiling Patterns of Density
A population density map of Africa reveals a striking contrast between densely populated areas and vast stretches of sparsely populated regions. The coastal zones, particularly along the Mediterranean Sea, the Nile River Valley, and the southern coast of the continent, showcase high population densities. These areas often benefit from fertile agricultural lands, access to water resources, and strategic locations for trade and commerce.
Conversely, the interior regions of Africa, especially the Sahara Desert and the Sahel, are characterized by low population densities. These regions face challenges such as arid climates, limited access to water, and often lack infrastructure and economic opportunities.
Beyond Numbers: Understanding the Drivers of Density
Population density is not merely a numerical indicator; it reflects a complex interplay of factors that shape human settlements. Several key drivers contribute to the spatial distribution of population in Africa:
- Environmental Factors: Topography, climate, and access to water resources significantly influence population density. Coastal areas, river valleys, and regions with favorable rainfall patterns tend to attract larger populations. Conversely, arid regions, mountainous terrains, and areas prone to natural disasters often exhibit lower population densities.
- Economic Opportunities: The presence of industries, agriculture, and other economic activities attracts people, leading to higher population densities in urban centers and industrial zones. Conversely, regions with limited economic prospects often experience outmigration, resulting in lower population densities.
- Historical Factors: Colonial legacies, migration patterns, and historical events have shaped the current population distribution in Africa. For instance, the forced migration of populations during the colonial era has left lasting impacts on population density patterns in various regions.
- Political Factors: Political stability, government policies, and infrastructure development play a significant role in attracting or deterring population growth. Areas with strong governance, infrastructure, and social services tend to have higher population densities.
The Significance of Population Density Maps
Population density maps serve as vital tools for various sectors, providing valuable information for:
- Urban Planning: Understanding population distribution helps city planners design sustainable urban environments, optimize infrastructure development, and address challenges related to housing, transportation, and public services.
- Resource Allocation: Population density maps aid in the efficient allocation of resources, including healthcare facilities, schools, and water infrastructure, ensuring equitable distribution based on population needs.
- Disaster Management: In the face of natural disasters, population density maps help identify vulnerable areas and facilitate targeted relief efforts.
- Economic Development: Understanding population distribution allows policymakers to tailor economic development strategies to specific regions, fostering growth and addressing regional disparities.
- Environmental Conservation: Population density maps can inform conservation efforts by identifying areas with high population pressure and potential ecological risks, facilitating targeted conservation strategies.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Population Density in Africa
Q: What is the average population density in Africa?
A: The average population density in Africa is approximately 40 people per square kilometer. However, this figure masks significant regional variations.
Q: Which countries in Africa have the highest population densities?
A: Countries with the highest population densities in Africa include:
- Rwanda: 507 people per square kilometer
- Burundi: 424 people per square kilometer
- Nigeria: 226 people per square kilometer
- Egypt: 102 people per square kilometer
- Ethiopia: 110 people per square kilometer
Q: Which countries in Africa have the lowest population densities?
A: Countries with the lowest population densities in Africa include:
- Namibia: 3 people per square kilometer
- Botswana: 4 people per square kilometer
- Libya: 4 people per square kilometer
- Mauritania: 4 people per square kilometer
- Chad: 12 people per square kilometer
Q: How does population density impact the environment in Africa?
A: High population density can lead to increased pressure on natural resources, deforestation, land degradation, and pollution. Conversely, low population density may result in underutilization of resources and economic stagnation.
Q: How does urbanization affect population density in Africa?
A: Urbanization is a major driver of population density shifts in Africa. As people migrate to urban centers for economic opportunities, cities experience significant population growth, leading to increased density.
Tips: Utilizing Population Density Maps for Effective Planning
- Consider multiple data sources: Combine population density maps with other geographic data, such as land cover, soil fertility, and access to water resources, for a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Analyze trends over time: Compare population density maps from different years to identify population shifts, migration patterns, and urbanization trends.
- Incorporate local knowledge: Collaborate with local communities and experts to understand the nuances of population distribution and the factors that influence density in specific areas.
- Engage in participatory planning: Involve stakeholders, including local communities, government agencies, and NGOs, in the planning process to ensure that population density maps are used effectively to address local needs and priorities.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Shaping Africa’s Future
Population density maps offer a valuable lens through which to understand the complex demographic landscape of Africa. By revealing patterns of population distribution and the factors that influence them, these maps empower planners, policymakers, and researchers to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, infrastructure development, and environmental protection. As Africa continues to experience rapid population growth and urbanization, the significance of population density maps will only grow, providing a critical tool for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the continent’s demographic transformation.


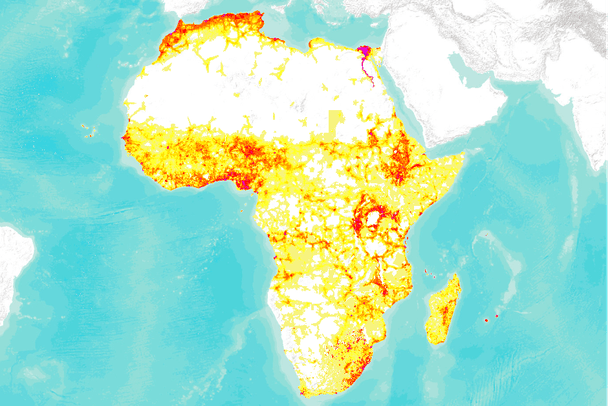
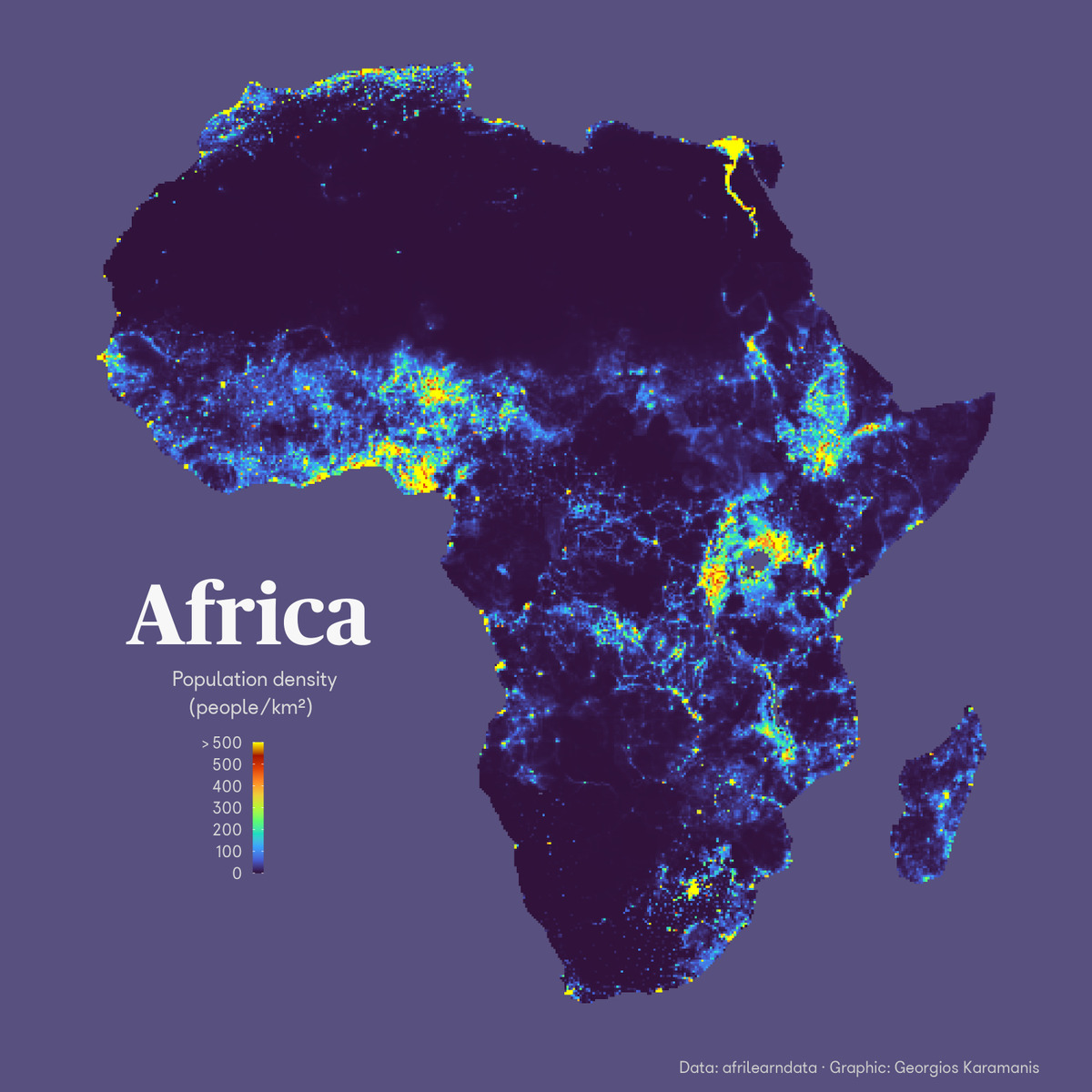
![Population density of Africa [800x747] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/4BQDENRGTDqwDlE92cyzRBY9eDu5L4tvAAWHFX5x-_A.png?auto=webpu0026s=2f6433d9b845209a827d26324205da0c6cca1f53)
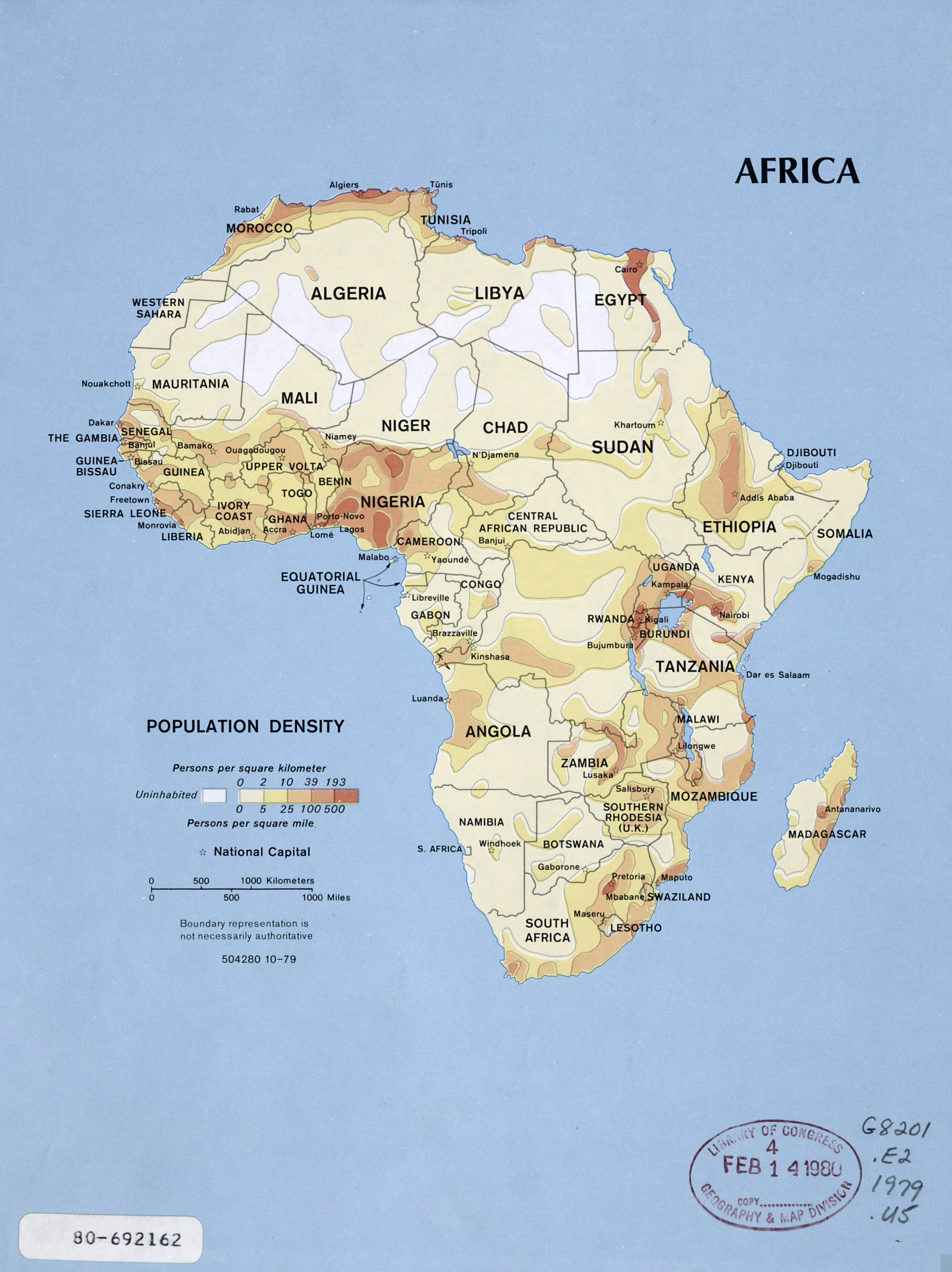
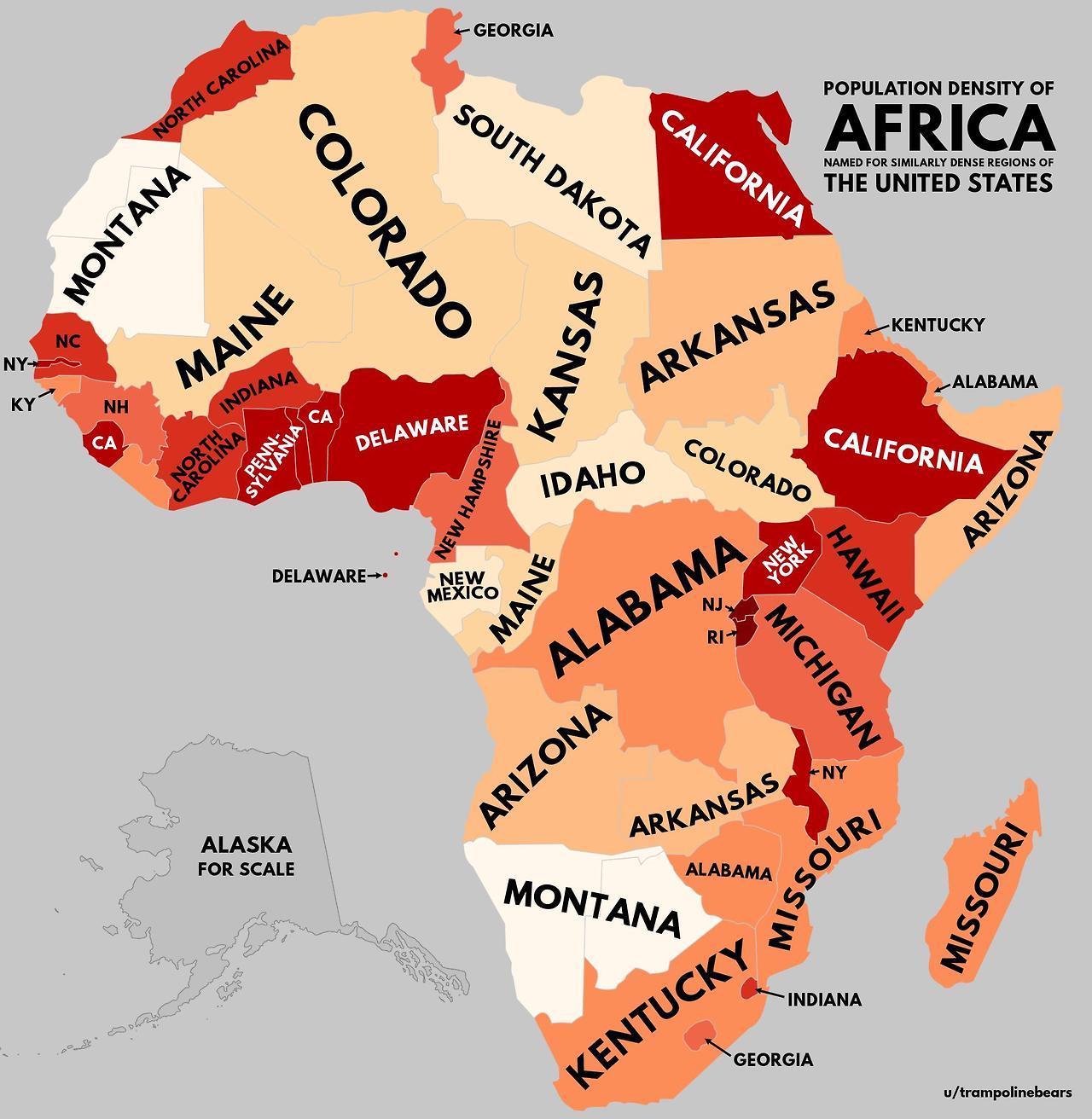

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking Africa’s Population Landscape: A Look at Density Maps and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!