The Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map: A Guide to Representation
Related Articles: The Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map: A Guide to Representation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map: A Guide to Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map: A Guide to Representation
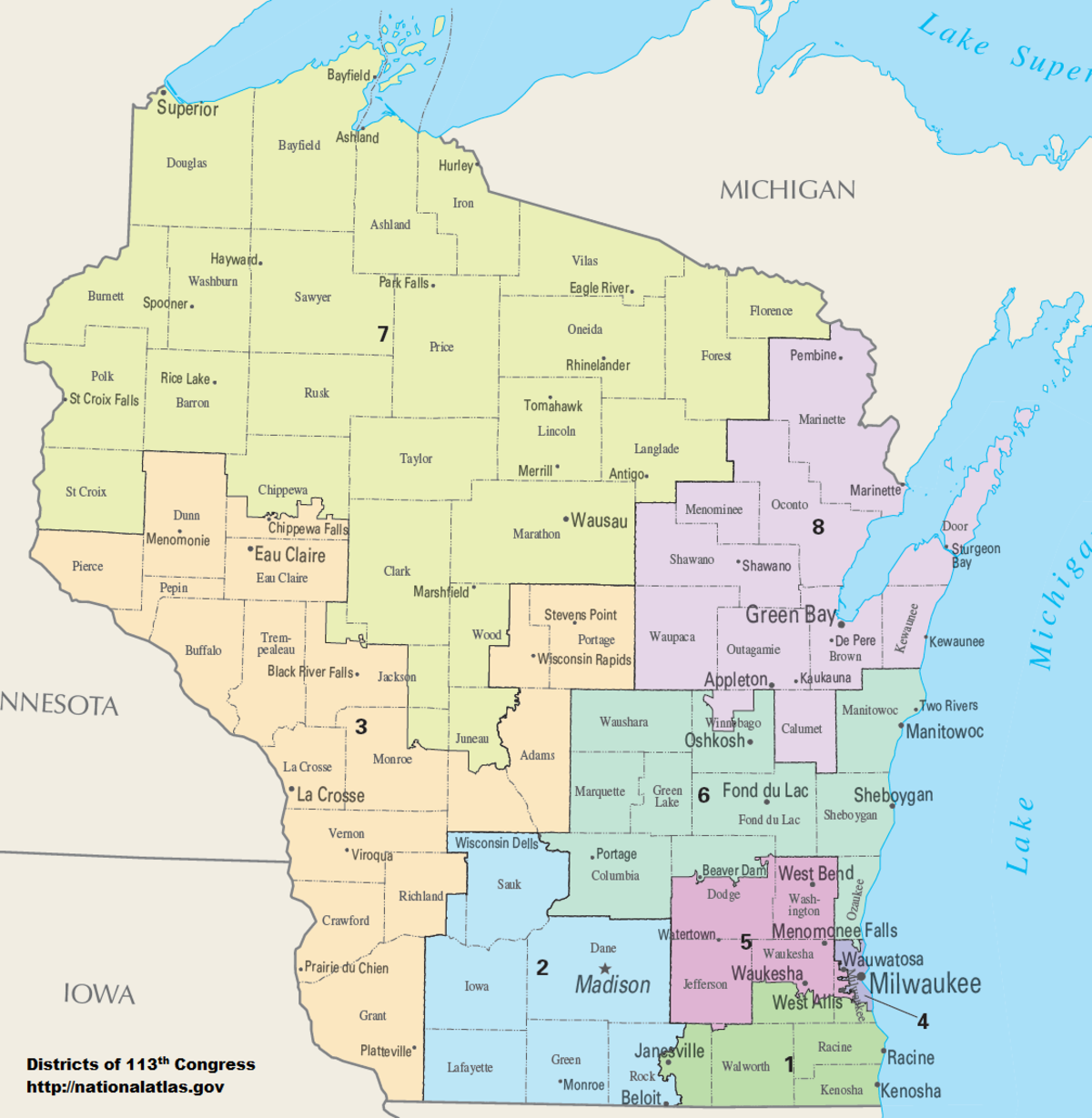
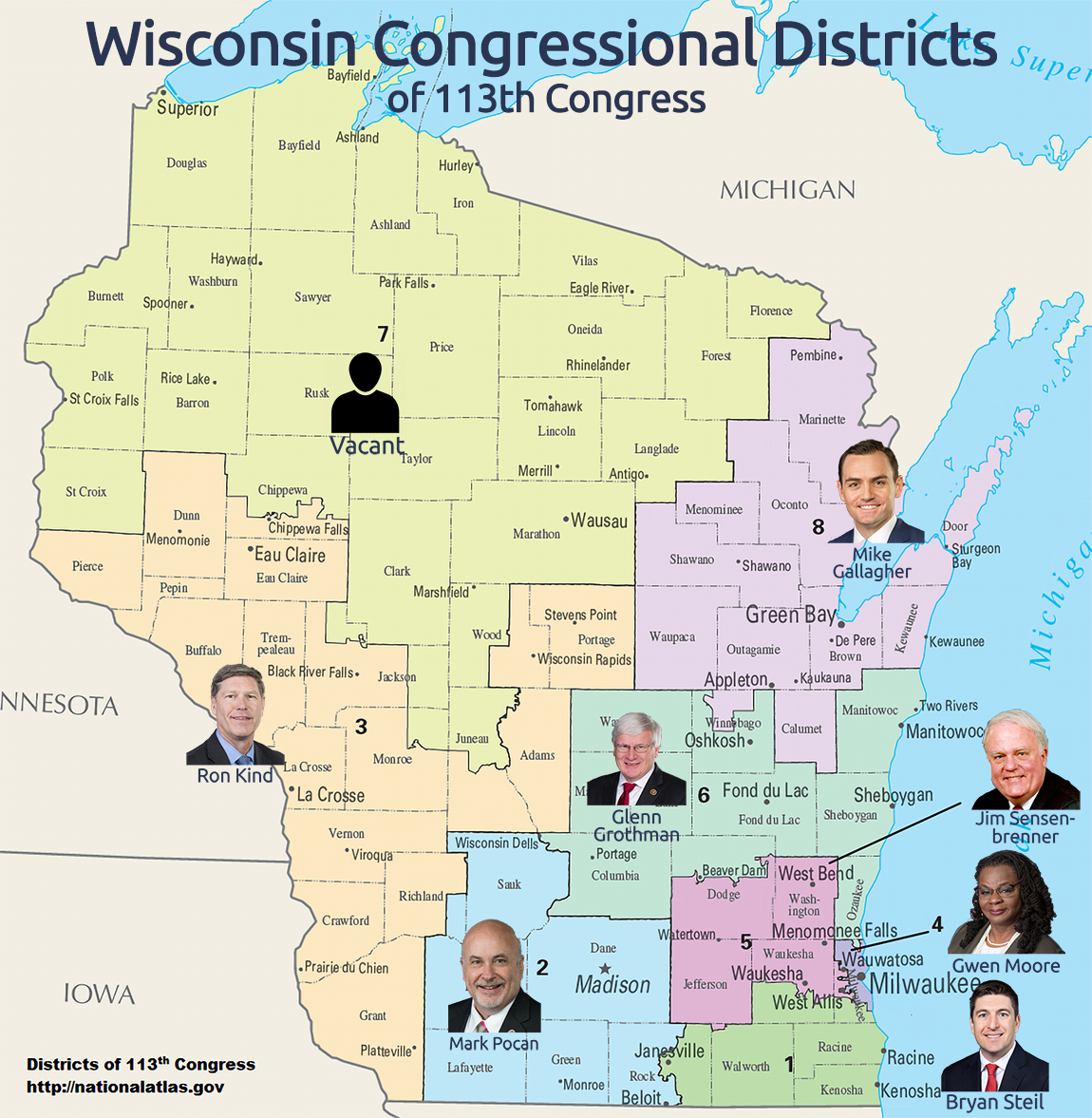
The Wisconsin congressional districts map is a crucial tool for understanding the state’s political landscape and its representation in the United States House of Representatives. This map, which is redrawn every ten years following the decennial census, defines the boundaries of the eight congressional districts that elect representatives to the U.S. Congress. Each district is assigned a specific number, ranging from 1 to 8, and is represented by a single member of Congress.
The map’s significance lies in its direct impact on the political power dynamics of the state. The way districts are drawn can influence the outcome of elections, determining which party has a majority in the House and shaping the legislative agenda. This underscores the importance of ensuring that the map is fair and representative of the diverse population of Wisconsin.
Understanding the Map:
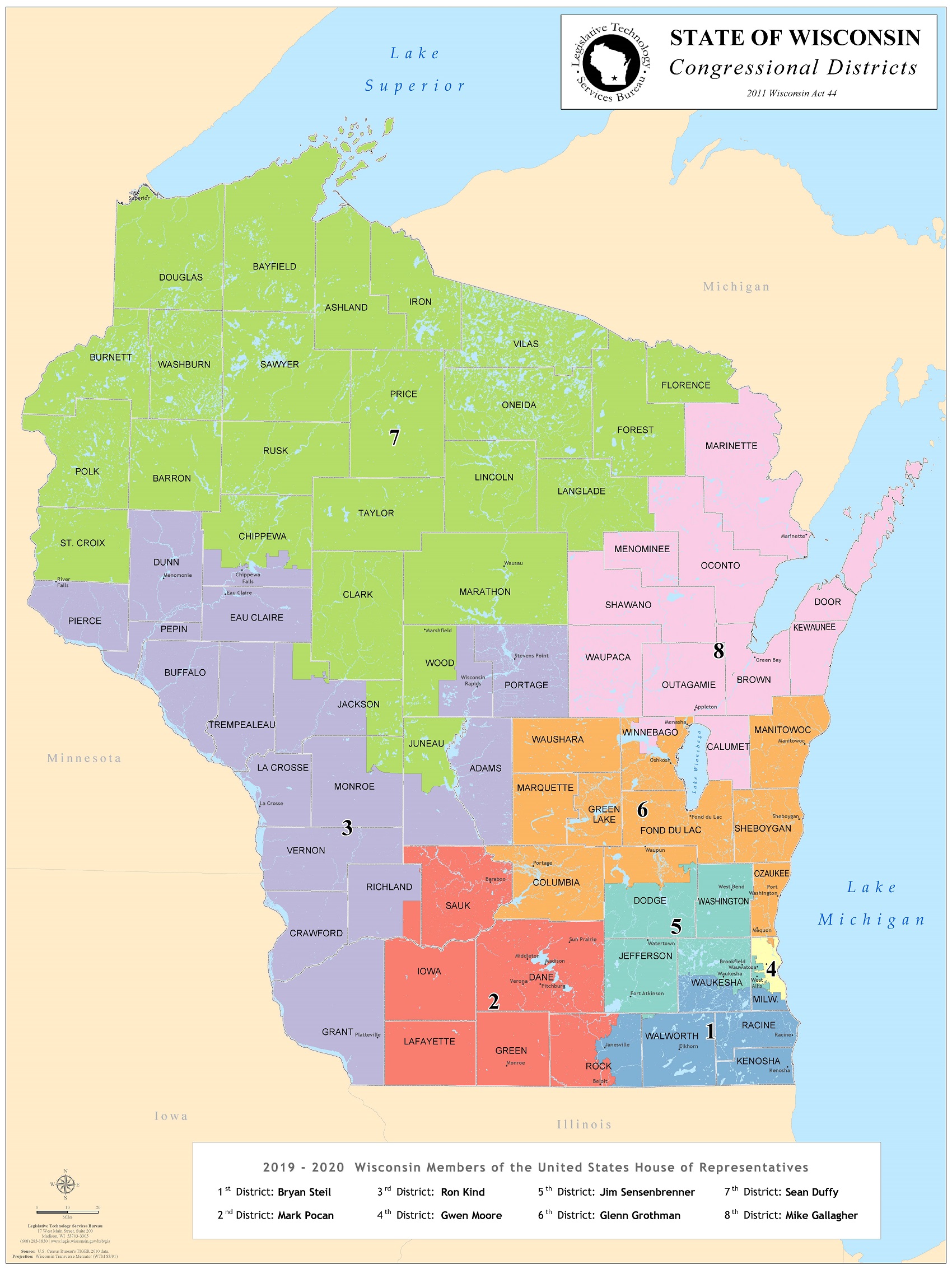
The current Wisconsin congressional districts map, established in 2011, reflects the results of the 2010 census. The map is composed of eight distinct districts, each with its unique demographic characteristics and political leanings.
- District 1: Located in the northwest corner of the state, this district encompasses the cities of Superior and Ashland and is known for its strong Democratic leanings.
- District 2: Stretching along the western border of Wisconsin, this district includes the cities of La Crosse and Eau Claire and generally leans Democratic.
- District 3: This district, covering the central and northern portions of the state, includes the city of Wausau and is considered a swing district, with both Democratic and Republican candidates having won in recent elections.
- District 4: Encompassing the Fox Valley region, this district includes the city of Appleton and is known for its Republican leanings.
- District 5: Located in the southeastern portion of the state, this district includes the city of Madison and is strongly Democratic.
- District 6: Covering the Milwaukee metropolitan area, this district is the most densely populated in Wisconsin and is generally considered a Democratic stronghold.
- District 7: This district, which includes the cities of Waukesha and Brookfield, is located in the western suburbs of Milwaukee and is known for its Republican leanings.
- District 8: Located in the southeastern portion of the state, this district includes the city of Racine and is generally considered a swing district.
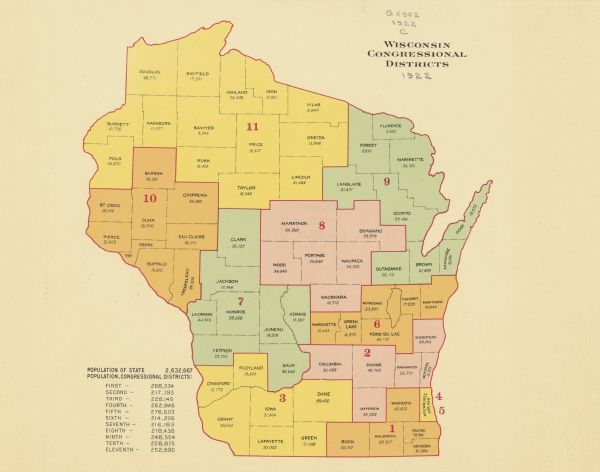
The Importance of Redistricting:
The process of redistricting, which involves redrawing congressional district boundaries, is a critical aspect of ensuring fair and equitable representation. The goal of redistricting is to create districts that are roughly equal in population and that reflect the diversity of the state’s population.
However, redistricting can be a politically charged process, as it often involves partisan maneuvering to create districts that favor one party over another. This practice, known as gerrymandering, can distort electoral outcomes and undermine the principle of one person, one vote.
The Impact of Gerrymandering:
Gerrymandering can have a significant impact on the political landscape of a state. By manipulating district boundaries, political parties can create districts that are heavily skewed in their favor, making it easier for their candidates to win elections. This can lead to a situation where one party holds a disproportionate number of seats in the legislature, even if they do not have a majority of the popular vote.
The Fight for Fair Maps:
In recent years, there has been a growing movement to reform redistricting processes and prevent gerrymandering. Advocates for fair maps argue that redistricting should be conducted in a nonpartisan manner, with input from the public and independent oversight. They also advocate for the use of independent commissions to draw district boundaries, rather than leaving the task to state legislatures.
FAQs about Wisconsin Congressional Districts:
Q: How often are Wisconsin congressional districts redrawn?
A: Congressional districts are redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for redrawing congressional district boundaries?
A: In Wisconsin, the state legislature is responsible for redrawing congressional district boundaries.
Q: What are the criteria for redrawing congressional districts?
A: Districts must be roughly equal in population and must not discriminate against any racial or ethnic group.
Q: How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
A: You can contact your state legislators and advocate for fair maps. You can also participate in public hearings and provide input on the redistricting process.
Tips for Understanding the Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map:
- Explore the map visually: Pay attention to the geographic boundaries of each district and the cities and towns they encompass.
- Research the demographic characteristics of each district: Understand the population size, racial and ethnic makeup, and socioeconomic characteristics of each district.
- Investigate the political leanings of each district: Analyze the voting history of each district and identify the dominant political party.
- Stay informed about redistricting efforts: Follow the news and participate in public hearings to stay informed about the process and advocate for fair maps.
Conclusion:
The Wisconsin congressional districts map is a vital component of the state’s political system, influencing the representation of its citizens in the U.S. House of Representatives. Understanding the map and the redistricting process is essential for ensuring fair and equitable representation. By advocating for nonpartisan redistricting and promoting transparency in the process, citizens can help ensure that the map accurately reflects the diversity and interests of the Wisconsin population.


![]()
![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Wisconsin Congressional Districts Map: A Guide to Representation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!