Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance in Southeast Asia
Related Articles: Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance in Southeast Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance in Southeast Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance in Southeast Asia
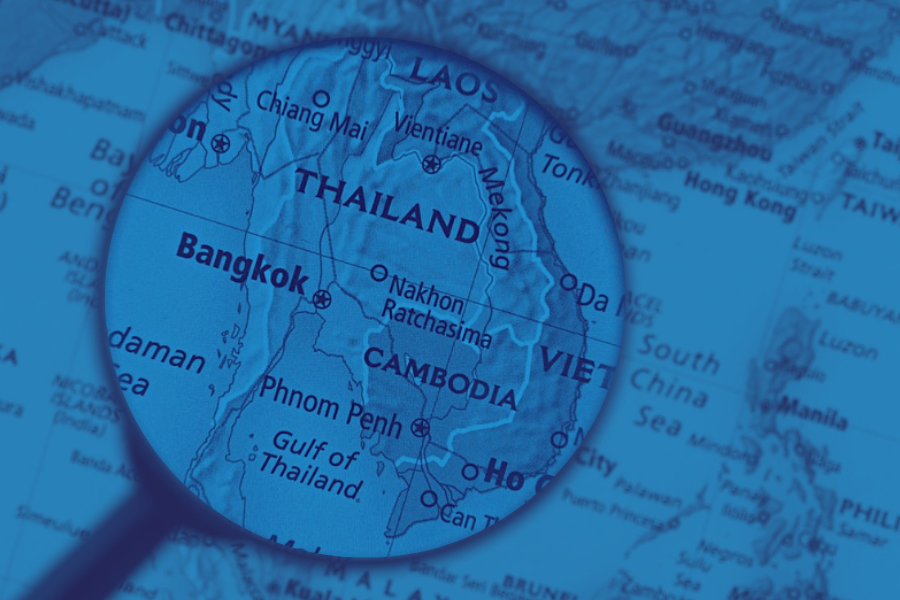
Thailand occupies a strategically important location in Southeast Asia, a region characterized by complex geopolitical dynamics and significant economic activity. Its geographical position acts as a bridge between mainland Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula, influencing regional trade, migration patterns, and political relationships for centuries. Analyzing its placement on the map reveals its crucial role in the region’s history and ongoing development.
The Kingdom’s geographical features contribute significantly to its strategic importance. Bordered by Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia, Thailand enjoys both land and maritime access to major trade routes. The Chao Phraya River, a significant waterway flowing through central Thailand, has historically facilitated internal trade and communication, connecting various regions to the Gulf of Thailand and the wider world. This natural infrastructure has played a vital role in shaping the country’s economic development and its connections with neighboring states. The extensive coastline along the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand further enhances its maritime connectivity, making it a key player in regional seaborne trade.
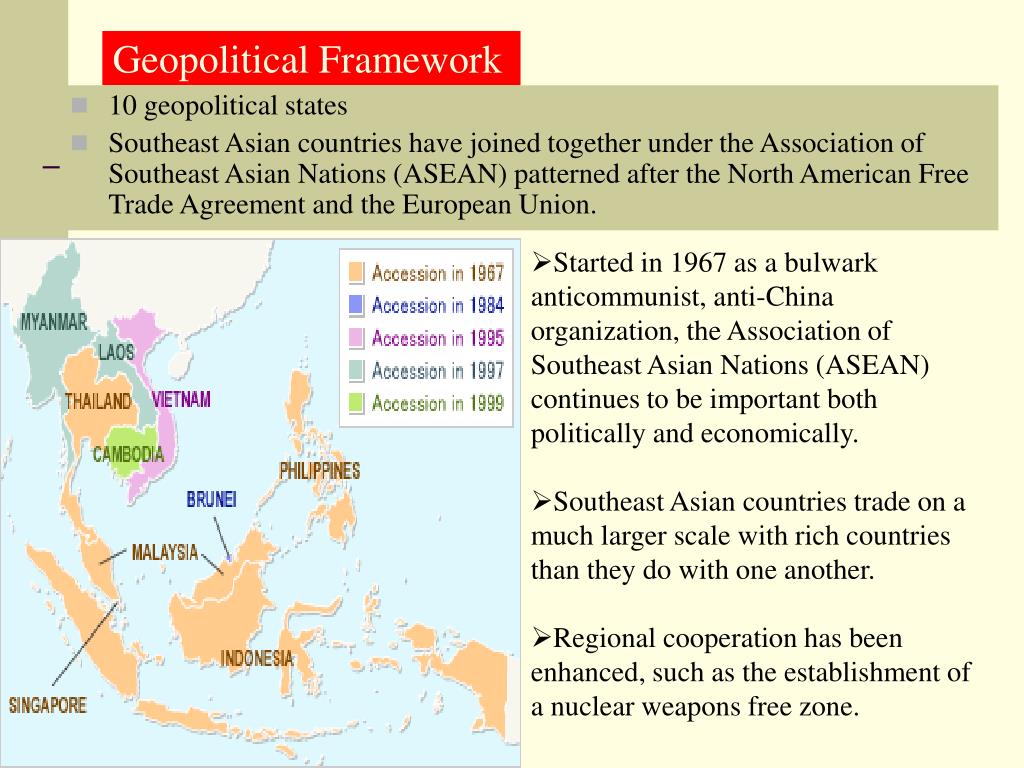
Thailand’s central location in Southeast Asia has facilitated its involvement in numerous regional and international organizations. Membership in ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) underscores its commitment to regional cooperation and integration. The nation’s participation in various economic initiatives, such as the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) program, demonstrates its engagement with regional development projects aimed at fostering economic growth and connectivity. This active participation reflects Thailand’s recognition of its role in shaping the future of the region.
Historically, Thailand’s geopolitical position has influenced its foreign policy. Its ability to maintain independence amidst the expansion of colonial powers in the 19th and 20th centuries highlights the strategic advantages of its location. The country’s skillful navigation of regional power dynamics has allowed it to avoid direct colonization, fostering a unique national identity and trajectory. This historical experience continues to shape its approach to international relations, emphasizing diplomacy and strategic partnerships.
The country’s geographical location also impacts its internal dynamics. The diverse geography, ranging from mountainous regions in the north to fertile plains in the central region and coastal areas in the south, contributes to regional variations in culture, economy, and social structures. These internal variations require effective governance and policies aimed at promoting national unity and equitable development across all regions. Managing these internal complexities while simultaneously engaging in regional and international affairs presents a significant challenge.
The country’s economy benefits significantly from its position. Its strategic location makes it a crucial hub for trade and transportation, serving as a gateway between East and West. The nation’s ports and infrastructure facilitate the flow of goods and services across Southeast Asia and beyond. This role as a transit point contributes to the nation’s economic growth and its integration into global supply chains. The tourism sector, a significant contributor to the economy, also benefits from this accessible location, attracting millions of visitors annually.
Furthermore, the nation’s geographical position influences its role in regional security. Its proximity to areas of potential conflict necessitates its active participation in maintaining regional stability. The country’s military and diplomatic efforts contribute to conflict resolution and peacekeeping initiatives, reflecting its understanding of its responsibilities within the Southeast Asian context. This commitment to regional security is essential for maintaining peace and promoting economic development within the wider region.
FAQs Regarding Thailand’s Geopolitical Position:
-
Q: How does Thailand’s geography affect its economic development? A: Thailand’s central location, navigable rivers, and extensive coastline facilitate trade, tourism, and the development of crucial infrastructure, contributing to economic growth and integration into global markets.
-
Q: What is Thailand’s role in regional security? A: Thailand actively participates in maintaining regional stability through diplomatic efforts and military cooperation, addressing potential conflicts and promoting peace within Southeast Asia.
-
Q: How does Thailand’s location influence its relationship with neighboring countries? A: Thailand’s position as a bridge between mainland Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula necessitates close relations with its neighbors, influencing trade, migration, and political cooperation.
-
Q: What are the challenges posed by Thailand’s geographical location? A: Managing internal regional disparities, navigating complex geopolitical dynamics, and addressing potential security threats are among the challenges arising from its strategic location.
-
Q: How does Thailand’s membership in ASEAN contribute to its geopolitical influence? A: ASEAN membership enhances Thailand’s role in regional decision-making, fostering economic cooperation and contributing to its influence within the Southeast Asian context.
Tips for Understanding Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance:
- Analyze Thailand’s historical interactions with its neighbors to understand the evolution of its regional role.
- Examine the country’s participation in regional organizations and initiatives to assess its commitment to regional cooperation.
- Study the country’s economic infrastructure and its contribution to regional trade and connectivity.
- Consider the impact of Thailand’s diverse geography on its internal dynamics and national development strategies.
- Evaluate the nation’s foreign policy and its approach to regional security challenges.
Conclusion:
Thailand’s location in the heart of Southeast Asia grants it significant geopolitical influence. Its central position, coupled with its historical experience, diverse geography, and active participation in regional organizations, establishes its crucial role in shaping the region’s economic, political, and security landscape. Understanding the interplay of these factors is essential for comprehending Thailand’s importance in the broader context of Southeast Asian development and global affairs. Further research into the nation’s historical trajectories, economic policies, and foreign relations will provide a more nuanced understanding of its multifaceted contributions to the region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Thailand’s Geopolitical Significance in Southeast Asia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!