Navigating Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Heat Maps
Related Articles: Navigating Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Heat Maps

In the realm of decision-making, uncertainty is a constant companion. Whether planning a business venture, launching a new product, or navigating a complex project, the potential for unforeseen circumstances looms large. To effectively manage this uncertainty, organizations rely on a powerful tool: the risk heat map.
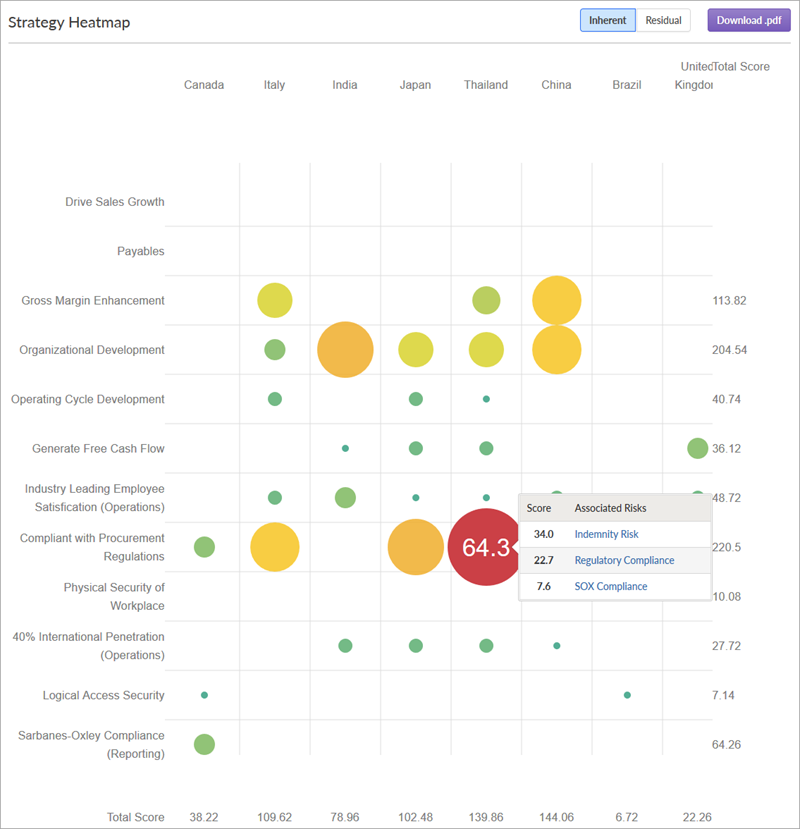
This visual representation, often depicted as a matrix or grid, provides a structured framework for identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing risks. By assigning each risk a level of impact and likelihood, the heat map creates a clear visual representation of the relative severity of each risk, enabling informed decision-making and risk mitigation strategies.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Impact and Likelihood
The core of the risk heat map lies in the interplay of two key factors: impact and likelihood.
- Impact: This refers to the potential consequences of a risk materializing. It can be measured in various ways, such as financial loss, reputational damage, operational disruption, or environmental harm.
- Likelihood: This quantifies the probability of a risk occurring. It can be assessed based on historical data, expert opinions, or industry trends.
By assigning each risk a score on both impact and likelihood scales, the heat map generates a clear visual representation of its severity. High-impact, high-likelihood risks are typically highlighted in red, signifying a critical need for immediate attention and mitigation strategies. Conversely, low-impact, low-likelihood risks might be depicted in green, indicating a lower priority for immediate action.
Constructing a Robust Risk Heat Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
The construction of an effective risk heat map requires a systematic approach:
1. Identify Potential Risks: This step involves brainstorming a comprehensive list of potential risks that could affect the project, initiative, or organization. It is crucial to consider a wide range of possibilities, encompassing both internal and external factors.
2. Define Impact and Likelihood Scales: Establish clear and consistent scales for measuring impact and likelihood. These scales should be tailored to the specific context and objectives of the analysis. Numerical scales, such as 1-5 or 1-10, are commonly used, with higher numbers representing greater impact or likelihood.
3. Assign Risk Scores: Once the scales are defined, each identified risk is assigned a score on both impact and likelihood. This process often involves expert judgment, historical data analysis, or a combination of both.
4. Plot Risks on the Heat Map: The assigned scores for each risk are then plotted on the heat map, creating a visual representation of their relative severity. The heat map typically uses a color gradient, with red representing high-impact, high-likelihood risks and green representing low-impact, low-likelihood risks.
5. Prioritize Risks: The heat map provides a clear visual framework for prioritizing risks. High-impact, high-likelihood risks should be addressed first, followed by those with moderate impact and likelihood. Lower-impact, lower-likelihood risks can be monitored and addressed as resources allow.
Beyond Visualization: Actionable Insights from Risk Heat Maps
The risk heat map is more than just a visual representation; it serves as a powerful tool for driving strategic decision-making and risk mitigation efforts. It offers several key benefits:
1. Enhanced Risk Awareness: The heat map provides a clear and concise overview of the organization’s risk landscape, promoting greater risk awareness among stakeholders. This awareness fosters a proactive approach to risk management, encouraging early identification and mitigation of potential threats.
2. Improved Risk Prioritization: By visually highlighting the relative severity of risks, the heat map enables organizations to prioritize their risk management efforts, focusing resources on the most critical threats. This ensures that limited resources are allocated effectively, maximizing the impact of risk mitigation strategies.
3. Facilitated Communication and Collaboration: The heat map serves as a common language for discussing risks across different departments and stakeholders. This shared understanding fosters collaboration and facilitates the development of comprehensive risk mitigation plans.
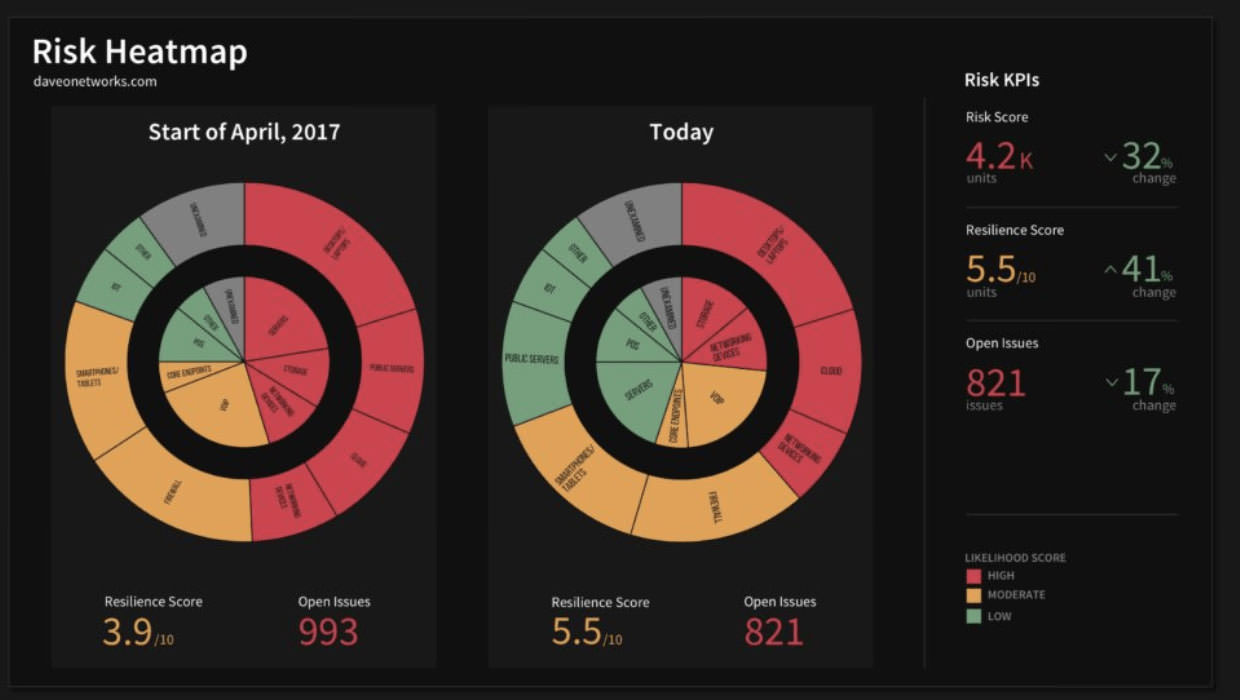
4. Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment: The risk heat map is not a static tool but rather a dynamic framework that can be updated and adjusted over time. As new risks emerge or existing risks change, the heat map can be recalibrated to reflect the evolving risk landscape, ensuring that risk management efforts remain relevant and effective.
Addressing Common Questions: FAQs on Risk Heat Maps
1. What are the limitations of a risk heat map?
While powerful, risk heat maps have limitations. They rely heavily on subjective assessments of impact and likelihood, which can be influenced by biases and differing perspectives. Additionally, they may not adequately capture complex interdependencies between risks or the potential for cascading effects.
2. How can I ensure the accuracy of my risk heat map?
Accuracy is paramount. Involve a diverse range of stakeholders with relevant expertise, use data-driven assessments where possible, and regularly review and update the heat map based on new information and changing circumstances.
3. Can a risk heat map be used for different types of projects?
Absolutely. Risk heat maps are versatile and can be adapted to suit various project types, including product development, business expansion, organizational change, and strategic planning.
4. What are some best practices for using risk heat maps effectively?
- Involve stakeholders: Engage relevant individuals from different departments and levels within the organization.
- Use clear and consistent scales: Define impact and likelihood scales that are specific to the context and objectives.
- Regularly review and update: Monitor the risk landscape and adjust the heat map as needed.
- Communicate effectively: Share the heat map with stakeholders and explain its implications.
Tips for Optimizing Risk Heat Map Effectiveness
1. Consider using a software tool: Specialized risk management software can automate the process of creating, updating, and analyzing risk heat maps.
2. Incorporate qualitative factors: While quantitative data is valuable, consider incorporating qualitative factors, such as expert opinions and stakeholder concerns, into the risk assessment process.
3. Use color coding effectively: Choose colors that are visually distinct and communicate the severity of risks clearly.
4. Develop a clear action plan: For each high-priority risk, develop a detailed action plan outlining mitigation strategies, responsibilities, and timelines.
Conclusion: Empowering Decision-Making Through Risk Awareness
The risk heat map serves as a valuable tool for navigating uncertainty, fostering a proactive approach to risk management. By providing a clear visual representation of the organization’s risk landscape, it empowers decision-makers to prioritize risks, allocate resources effectively, and mitigate potential threats. Through its ability to enhance risk awareness, improve communication, and facilitate collaboration, the risk heat map plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of projects, initiatives, and organizations operating in complex and dynamic environments.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
